Why LED Lighting?
LED Lighting is the future of lighting because unlike incandescent and fluorescent lighting, LEDs consume up to 90% less energy than other sources, use no toxic chemicals and are made of materials that can be recycled. Beyond the significant cost savings LEDs provides, this light source is the ultimate in planet friendly technology…a truly “green” product.
The Environment – Keeping it Green
i. Our planet is in crisis. We’ve been wasting natural resources while at the same time failing to bring more efficient solutions into use. Interest groups, governments, consumers and now businesses have realized that there are actions that can be taken to save the planet, and the commitment to “going green” is increasing. One acknowledged way to easily be part of the green movement is shining on us every day…at home, at work, and in public facilities, lighting is a necessity in our lives. Traditional lighting sources are under close scrutiny. The days of incandescent lighting are soon coming to an end. Even florescent lighting will soon become unwelcomed. These light sources that consume excessive energy, contaminate landfills with toxic waste, and generate excessive heat will soon give way to new, superior technology…LED technology.
ii. The momentum to “save the planet” with the financial backing of countless government-funded stimulus programs is accelerating opportunities in what would normally be an evolutionary market segment. With increasing awareness of “green” initiatives and new legislation driving energy efficiency, the changeover to economical lighting options is driving change. By 2012 government legislation will make incandescent lighting a thing of the past. Solid-state technologies now provide the environmentally safe and energy efficient solutions to become the new dominant lighting source. Over the past 20 years the technology of light emitting diodes (LED) has expanded at a frantic pace and is now available in industrial strength applications delivering higher quality, lower cost lighting solutions in commercial, institutional and residential environments. There is tremendous interest within the Department of Energy as well as state and local governments to move from traditional lighting sources to LED lighting alternatives and to incent commercial enterprises to do the same.
- i. Long Life Means Less Waste
- ii. Uses Fewer Kilowatts of Power
- iii. No mercury or other dangerous gases
What is LED Light?
i. LEDs (light emitting diodes) are solid-state lighting devices that produce light when a forward voltage is applied. An LED consists of a semiconductor diode packaged in a clear epoxy or silicone gel. The diode contains two slightly different materials: a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor. The P-type semiconductor has “holes” created by a lack of electrons, producing a positive charge. Conversely, the N-type material has an excess of electrons, resulting in a negative charge. The P- and N-type semiconductors are placed in direct contact in the diode and the region where they meet is referred to as the PN junction. When an electric current passes through the device, electrons flow toward the P region and holes flow toward the N region. Near the PN junction, electrons and holes combine and the electrons shed the extra energy they acquired from the electric current. This energy is released in the form of a photon, the basic unit of light. In this way, an LED emits visible light.
ii. The energy of the photons corresponds to the color of the light emitted. In the visible light spectrum, blue and purple light results from the greatest energy emission whereas yellow and red light is a result of the lowest energy emission. By utilizing materials with different band gaps, engineers can alter energy emission and thus the color of light produced by an LED.
Why LED technology now?
i. LED technology has been around for decades, used as indicator lights on electronic devices and then as decorative lighting. While commercial and residential LED lights have been in development for years, finally the advances in technology are at a point where LED lighting is industrial strength and ready for commercial use. Not only is the quality high with life expectancy of 30,000 to 50,000 hours, being covered by manufacturer warranties, but energy savings levels have become compelling. LED lighting is indeed ready for prime time.
ii. LED lighting is the future of lighting because unlike incandescent and florescent lighting, LED’s consume up to 90% less energy than other sources, use no toxic chemicals and are made of materials that can be recycled. Besides the significant cost savings of LED lighting, this light source is the ultimate in planet friendly technology…a truly “green” product.
Key Features of LED Lighting
Here are a few of the important features of LED lights:
- i. A solid state light technology made with Light Emitting Diodes
- ii. More energy efficient that incandescent, fluorescent, or other lights
- iii. Operates at a much lower temperature (cool to the touch)
- iv. Environmentally Friendly
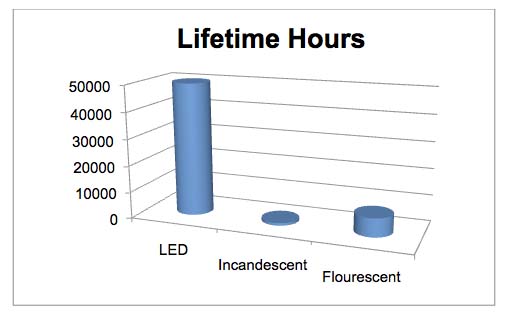
- v. Durable and capable of long hours of use (see chart)
 |
Important Benefits of LED Lighting:
Along with the technology LED lighting offers many direct benefits to the users.
- Up to 90% energy savings
- Cool operating
- Long life 50,000 hrs
- Eliminates frequent light maintenance
- No mercury – No UV rays
- Accurate color rendering
- Reduce eye strain – Headaches
- Long warranties
- No ballasts required – No hum or flickering
- Easy to install – Uses existing fixtures
- Made of recyclable materials
FAQ’s
-
- Why LED’s?
As a rule, LED bulbs use 90% less electricity than standard bulbs. They have an unparalleled even spectrum of light and have a lifespan beyond ten years. LED’s provide the most efficient way to save energy and conserve natural resources. If LED’s were implemented right now universally, not another power plant would need to be built. LEDs would actually eliminate the need for over 30 existing power plants!
-
- Do LED light bulbs contain mercury?
No. LED bulbs do not contain mercury. They can actually be recycled as they do not contain hazardous substances and are manufactured without hazardous substances.
-
- How do LED light bulbs compare to CFL bulbs?
Studies show LED light bulbs use 50% less energy than CFL bulbs and in many cases last 10 times longer than CFL light bulbs. They are much more durable, environmentally friendly, vibration and shock resistant and offer excellent light quality (both indoor and outdoor), and variability in light color.
-
- Do LED bulbs produce as much heat as CFL or Incandescent bulbs?
LED light bulbs emit much less heat than a CFL or incandescent bulb. In most cases, one can actually feel the temperature difference just by being near the light. LED light bulbs will always operate at a lower temperature than a CFL or incandescent which has immediate benefits in reduced cooling bills where air conditioning is used.
-
- Why are LED lights more expensive?
LED light bulbs use an actual circuit board to operate and are made of electronic components. Essentially, they could be considered an electronic device. This technology continues to improve and gain advantages almost daily. The manufacturing and supply/demand of general lighting products are gearing up today, and costs will continue to decline as the adoption rate of LED Lighting increases. Through energy and replacement cost savings, LED lights have a short, measurable return on investment.
-
- Is LED light a different type of light?
Yes, LED light is said to be a safer, healthier light. LEDs do NOT produce any sort of ultraviolet radiation which causes rashes and other skin disorders, fabric fading, color fading in art, carpeting and other soft goods. LED lights produce none of the ‘buzzing’ or ‘flickering’ to which many people are sensitive. Residential and especially commercial and industrial plants, stores, libraries, galleries, and warehouses can immediately benefit from LED Lighting.
-
- How long do LEDs for general lighting really last?
LED’s are Solid State devices (SSL – or “solid state lighting”); they will not burn out like a filament type bulb. LED lights are typically rated to last about 50,000 hours. An incandescent light bulb is rated for about 1000 hours. CFLs or Fluorescent Tube lights are rated for 6-8000 hours. The product replacement cost math is easy: (see chart above) this also drastically reduces maintenance costs for facilities workers to replace lights or ballasts.